Home About Casts Theory Verifications References Contact FAQ
Verification fly rod, dynamic
The verification procedure for dynamic rod
properties is presented below for one specific rod
(serving as an example).
The dynamic properties of a fly rod are
modeled using:
· The bending stiffness and mass distributions giving the
frequencies with which the rod oscillates. During practical casting a fly line
is retained to the rod by the guides adding to the effective mass per unit
length of the rod (reducing the oscillation frequencies).
· The damping due to air drag and due to the fly line oscillating
with the rod. The damping gives the rate of decay of oscillation amplitude.
The
distributions for bending stiffness, outer diameter and mass density are
presented below:
Note: Mass density incl. the fly line was
used in the dynamic verifications below.

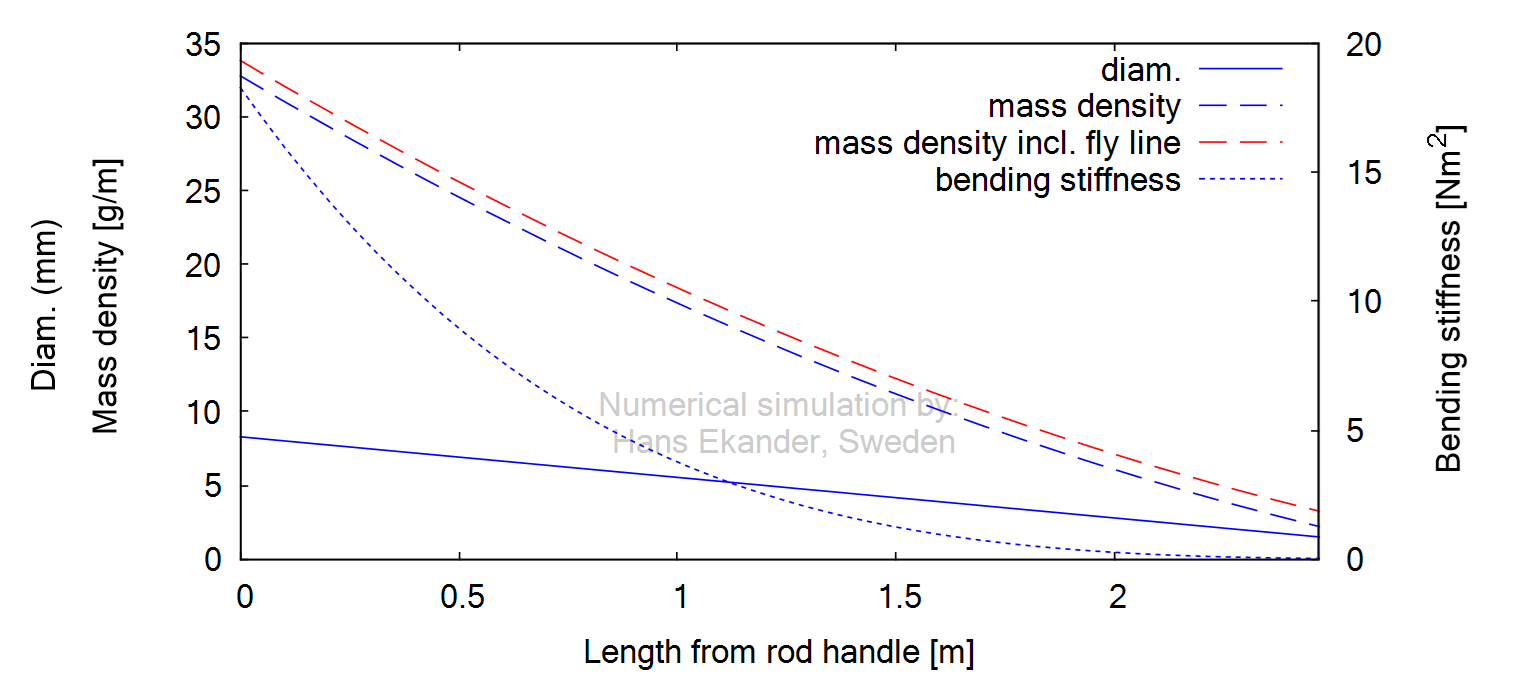
The verification of the bending stiffness
distribution is explained in “Static verification of fly rod”. The mass
distribution was determined by weighing the individual parts of the rod (and
the center of mass) and fitting a distribution. The damping due to the fly line
oscillating with the rod (and due to internal friction) is modeled using a
relaxation time, see Theory
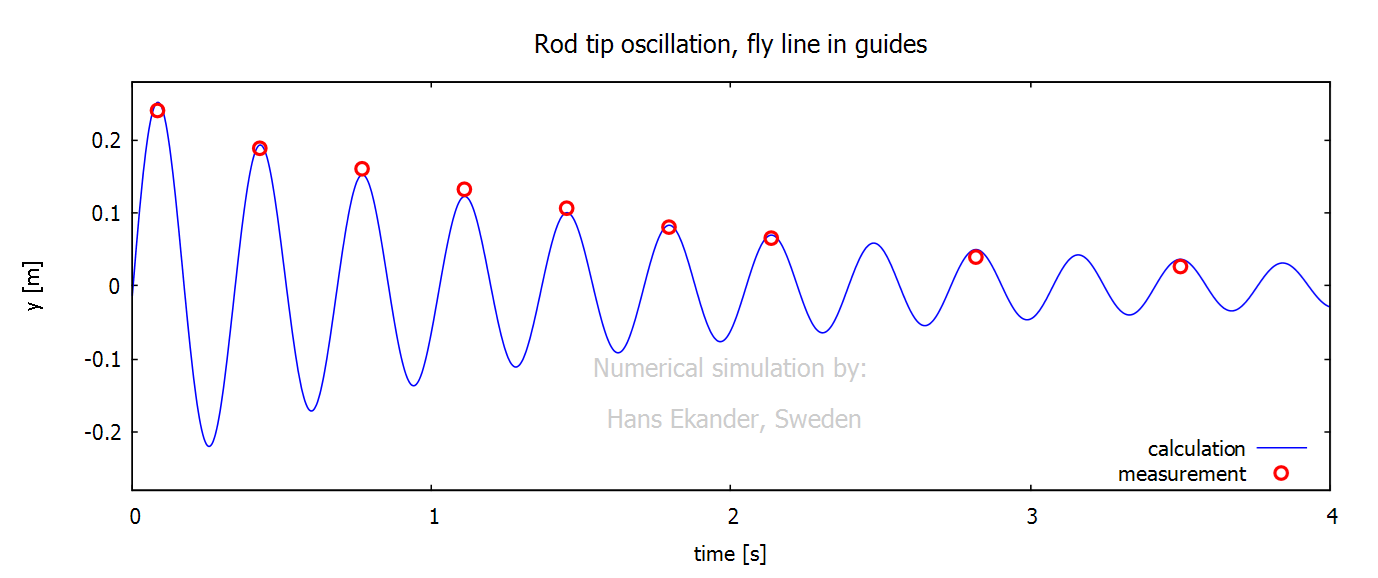
Verification of the dynamical fly rod
properties was done as follows:
· The rod handle was fixed in a vice.
· A fly line was held to the rod by the guides.
· Oscillations in the rod were initiated by hand (lowest
eigenfrequency).
· The oscillating rod was filmed, and the rod tip positions were
measured as the rod tip amplitude decreased with time.
The results are presented below verifying
that:
· the calculated oscillation frequency agrees with the measured.
· the calculated rate of decay of the rod tip amplitude agrees
with the measured.